Current issue
Special Feature : Frontier of Analysis for Electrode Surface
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Preface
-
Article type: Preface
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 203
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (363K)
Special Feature : Frontier of Analysis for Electrode Surface
-
Article type: Introduction
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 204-205
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (250K) -
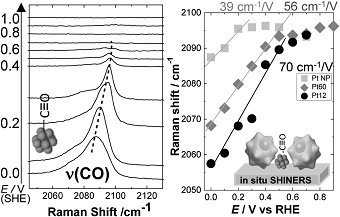
 Article type: Current Topics
Article type: Current Topics
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 206-211
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
-
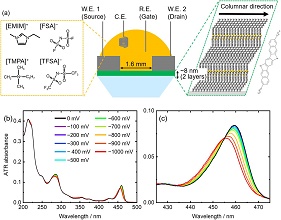
Article type: Current Topics
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 212-217
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (2880K) -
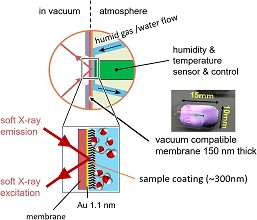
Article type: Current Topics
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 218-223
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (4985K) -
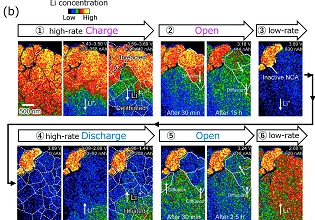
Article type: Current Topics
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 224-228
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (7442K) -
Article type: Current Topics
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 229-232
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (7151K) -
Article type: Current Topics
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 233-237
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (2564K)
Report
Conference Report
-
Article type: Report
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 238
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (563K) -
Article type: Report
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 239
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (663K) -
Article type: Report
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 240
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (1201K) -
Article type: Report
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 241
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (762K)
Science Café
Award winner
-
Article type: Science Café
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 242
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (391K) -
Article type: Science Café
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 243
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (787K) -
Article type: Science Café
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 244
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (759K)
Diversity Promotion
-
Article type: Science Café
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 245-246
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (1126K)
News & Trends
-
Article type: News & Trends
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 247
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (328K)
-
Article type: Bookstand
2024 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 248
Published: May 10, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 10, 2024
Download PDF (235K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|