Study on Electromagnetic Performance of Permanent Magnet Rotor and Dual Stator Starter Generator for Electric Vehicle Range Extender
Mingling Gao
,
Zhenhai Yu
,
Wenjie Jiao
,
Wenjing Hu
,
Huihui Geng
,
Yixin Liu
,
Shiqiang Liu
and
Yishuo Liu
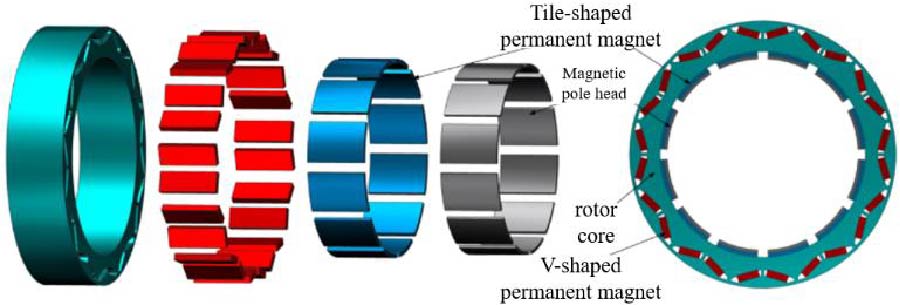
The flywheel-type dual-stator permanent magnet starter generator combines engine flywheel and starter generator rotor into a single unit, which has the advantages of high efficiency, high power density, and compact structure. This paper proposes a new type of dual-stator permanent magnet starter generator topology in which the two stators are concentric and share the same permanent magnet rotor. Equivalent magnetic circuit modeling of the inner stator's magnetic field, outer stator's magnetic field, and synthetic magnetic field using the equivalent magnetic circuit method list the system of flux equations and solve the main magnetic flux, leakage flux, and leakage coefficient, and the results show that the equivalent magnetic circuit method has smaller error and higher accuracy than the finite element method. The harmonic electric potential of the starter generator is modeled and analyzed. The permanent magnet rotor and inner and outer stator structures are optimized to obtain the optimal parameters, and the prototype is manufactured and tested. The optimized starter generator no-load induced electromotive force fundamental amplitude is improved. The induced electromotive force harmonic distortion rate is reduced, and the output performance of the whole generator is significantly improved.